The Top 5 Pros And Cons Of Self-Adhesive Bandages.Self-adhesive bandages have revolutionized wound care, offering a blend of convenience and effectiveness. Here, we explore the top advantages and drawbacks of these versatile bandages.
Pros of Self-Adhesive Bandages

Convenience and Ease of Use
Self-adhesive bandages, also known as self-stick bandages or sticky bandages, are designed for hassle-free application. Unlike traditional bandages requiring clips or tapes, these bandages feature an adhesive property that allows for effortless attachment to the skin.
Versatility in Application
One of the significant advantages lies in their versatility. These bandages adapt well to different body parts and contours, ensuring a snug fit without compromising movement or comfort. Whether for a finger, elbow, or knee, they conform easily, providing optimal coverage.
Breathability and Comfort
Many self-adhesive bandages are crafted from breathable materials, facilitating air circulation while offering protection. This feature aids in maintaining a conducive environment for wound healing, reducing the risk of moisture buildup and potential complications.
Promotes Healing and Support
These bandages offer support to injured areas, aiding in stabilization and reducing movement that may impede the healing process. Their pressure can assist in managing swelling or edema around wounds, promoting a conducive environment for recovery.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to alternative wound dressings or wraps, self-adhesive bandages are generally more cost-effective. Their availability in various sizes and quantities makes them an affordable option for minor injuries and wound care.
Cons of Self-Adhesive Bandages
Potential Skin Irritation
Some individuals may experience skin irritation or allergic reactions due to the adhesive components present in these bandages. It’s essential to conduct a patch test or seek medical advice if sensitivity is a concern.
Difficulty in Repositioning
Once applied, repositioning self-adhesive bandages can be challenging without losing their adhesive strength. Misplacement during application might lead to wastage or inadequate coverage.
Limited Compression Ability
Unlike certain specialized bandages, self-adhesive ones offer limited compression, making them less suitable for managing certain types of injuries that require consistent pressure application.
Adhesive Residue
Upon removal, these bandages may leave behind adhesive residue on the skin, requiring gentle cleaning to avoid discomfort or potential skin reactions.
Not Suitable for All Wounds
While versatile, self-adhesive bandages might not be suitable for all wound types. Deep, heavily bleeding, or infected wounds may require alternative and more absorbent dressing options.
Best Practices for Using Self-Adhesive Bandages
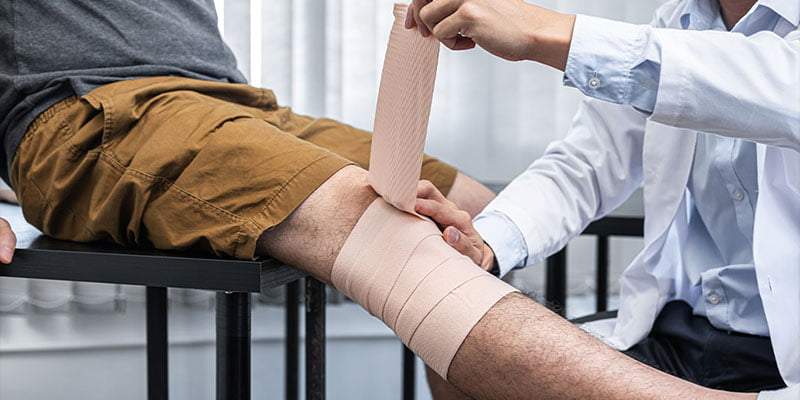
To maximize the benefits and minimize the drawbacks, ensure proper application by cleaning the wound area, avoiding excessive tension during wrapping, and monitoring for any adverse reactions.
In real-life scenarios, individuals have found self-adhesive bandages to be incredibly useful for minor cuts, abrasions, and sprains. However, in cases of extensive injuries or those requiring specialized care, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
Experts recommend incorporating self-adhesive bandages into first aid kits for their convenience and rapid application. However, they also emphasize the importance of understanding their limitations and seeking appropriate medical assistance for severe injuries.
The future of self-adhesive bandages seems promising, with ongoing research focusing on improving adhesive technologies and enhancing their effectiveness across a broader spectrum of wound care.
In conclusion, self-adhesive bandages offer a convenient and cost-effective solution for minor injuries, providing support and promoting healing. While they come with certain limitations, their versatility and ease of use make them a valuable addition to any first aid kit.
| Best Practices for Using Self-Adhesive Bandages |
|---|
| Clean the Wound Area |
| Thoroughly cleanse the wound and surrounding skin with mild soap and water. Ensure the area is dry before applying the bandage. |
| Proper Application Technique |
| Begin by gently placing the bandage over the wound, ensuring it covers the entire affected area. Avoid stretching the bandage excessively to prevent constriction. |
| Avoid Excessive Tension |
| Apply the bandage with the right amount of tension—neither too loose nor too tight—to allow for proper blood circulation without compromising the bandage’s adhesive properties. |
| Monitor for Adverse Reactions |
| Keep an eye on the skin under the bandage for any signs of irritation, redness, or discomfort. If any adverse reactions occur, remove the bandage and consult a healthcare professional. |
| Replacement and Removal |
| Change the bandage regularly, especially if it gets wet or dirty. To remove, slowly peel it off in the direction of hair growth to minimize skin irritation. Gently cleanse the area post-removal if adhesive residue remains. |
FAQs
- Are self-adhesive bandages waterproof?
Self-adhesive bandages vary in their water-resistant properties. Some are designed to be water-resistant, while others may lose their adhesive strength when wet. - Can self-adhesive bandages be reused?
Reusing self-adhesive bandages is not recommended as it may compromise their adhesive properties and hygiene. - Are self-adhesive bandages suitable for sensitive skin?
Individuals with sensitive skin should conduct a patch test before prolonged use. Some may experience irritation due to the adhesive. - How long can self-adhesive bandages stay on?
The duration varies depending on the brand and type of bandage. Generally, they can stay on for a few days if properly applied and if the wound does not require frequent checks. - Can self-adhesive bandages be used for large wounds?
Self-adhesive bandages are more suitable for smaller wounds. Large wounds may require specialized dressings or medical attention.



